Using Hasura Cloud with an AWS RDS Aurora Postgres database¶
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Step 0: Sign up or log in to Hasura Cloud
- Step 1: Create a Hasura Cloud project
- Step 2: Create an Aurora DB on AWS RDS (skip if you have an existing DB)
- Step 3: Allow connections to your DB from Hasura Cloud
- Step 4: Construct the database connection URL
- Step 5: Finish creating the Hasura Cloud project
- Step 6: Launch Hasura console
- Next steps
Introduction¶
This guide explains how to connect a new or existing AWS RDS Aurora Postgres database to a Hasura Cloud project.
Step 0: Sign up or log in to Hasura Cloud¶
Navigate to Hasura Cloud and sign up or log in.
Step 1: Create a Hasura Cloud project¶
On the Hasura Cloud dashboard, create a new project:
You will get prompted for a Postgres Database URL. We will create this in the next step and then come back here.
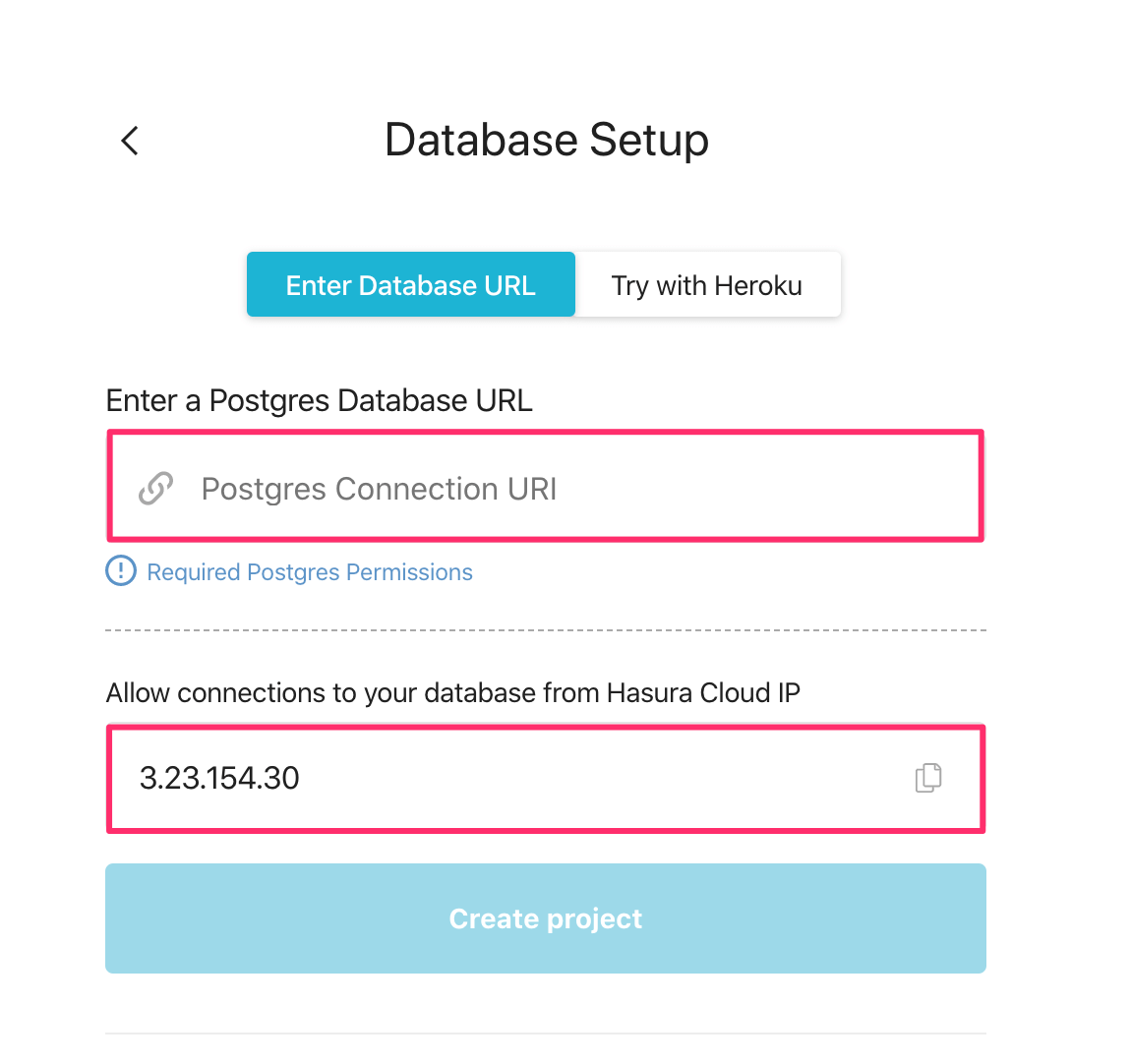
Also, copy the Hasura Cloud IP for later.
Step 2: Create an Aurora DB on AWS RDS (skip if you have an existing DB)¶
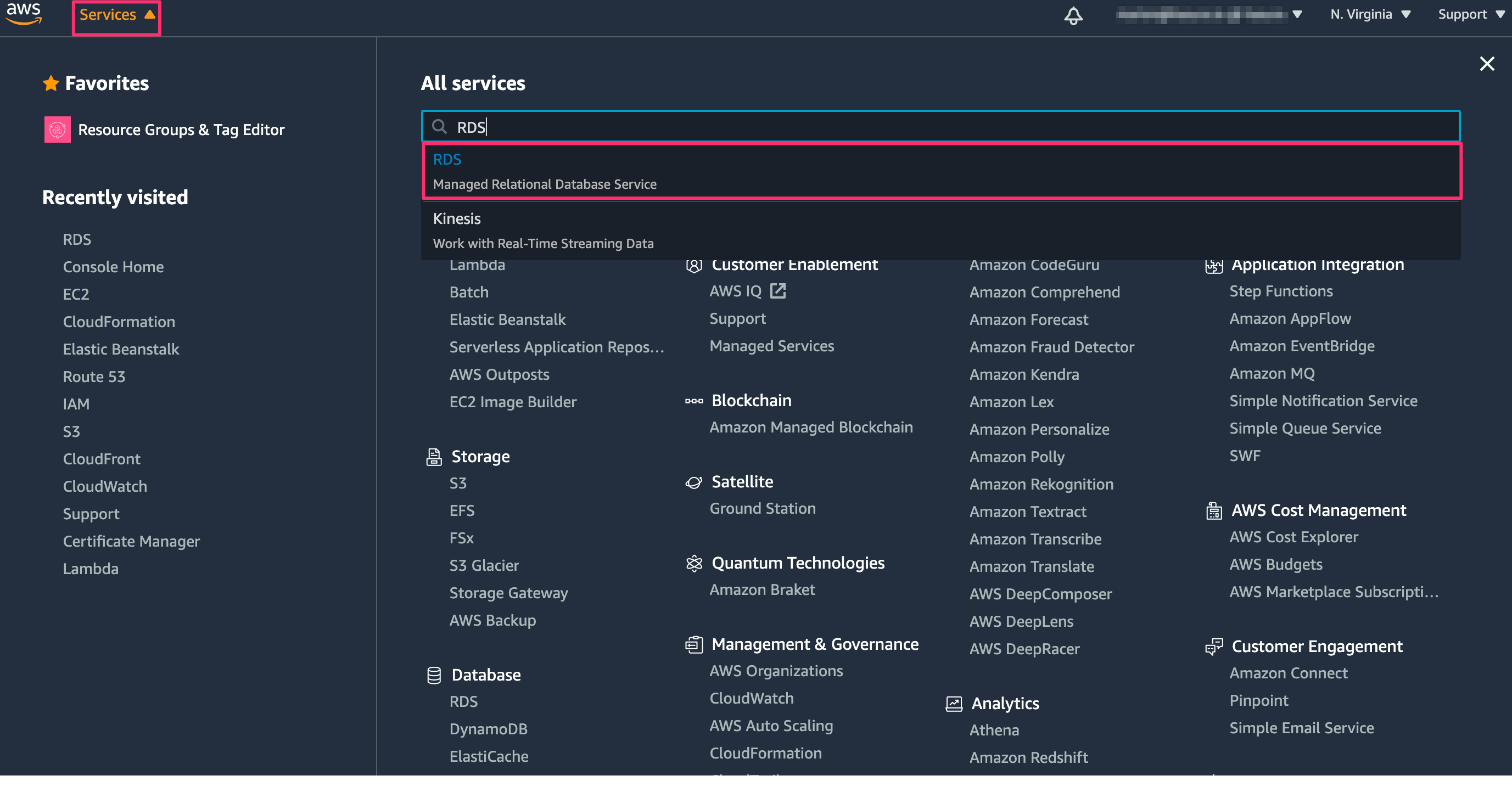
Log into the AWS console.
On the top left, click on Services and type “RDS” into the search field. Then click on RDS:
Click on the Create database button:
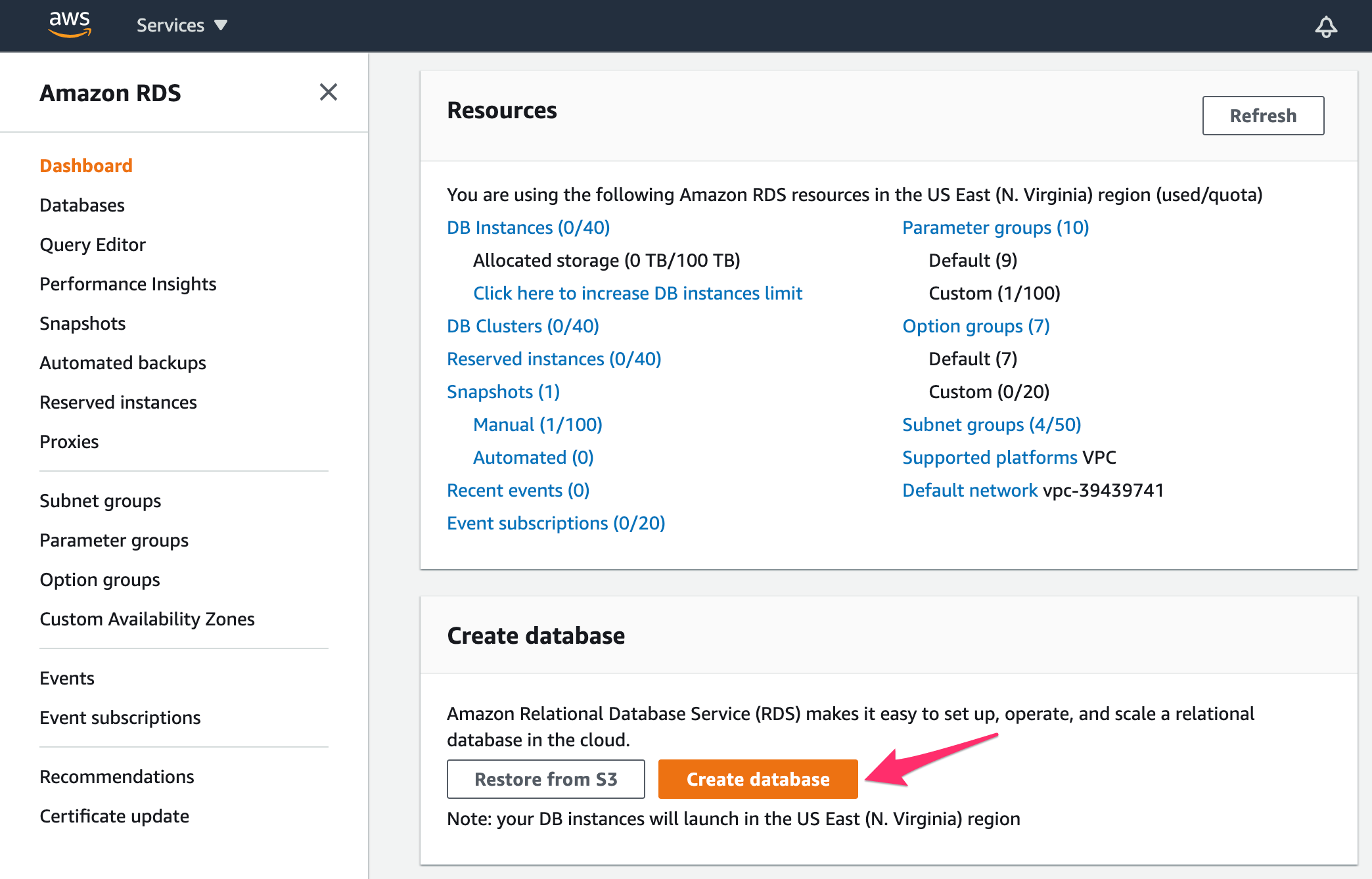
In Engine options, select Amazon Aurora as Engine type. Also, select Amazon Aurora with PostgreSQL compatibility as Edition:
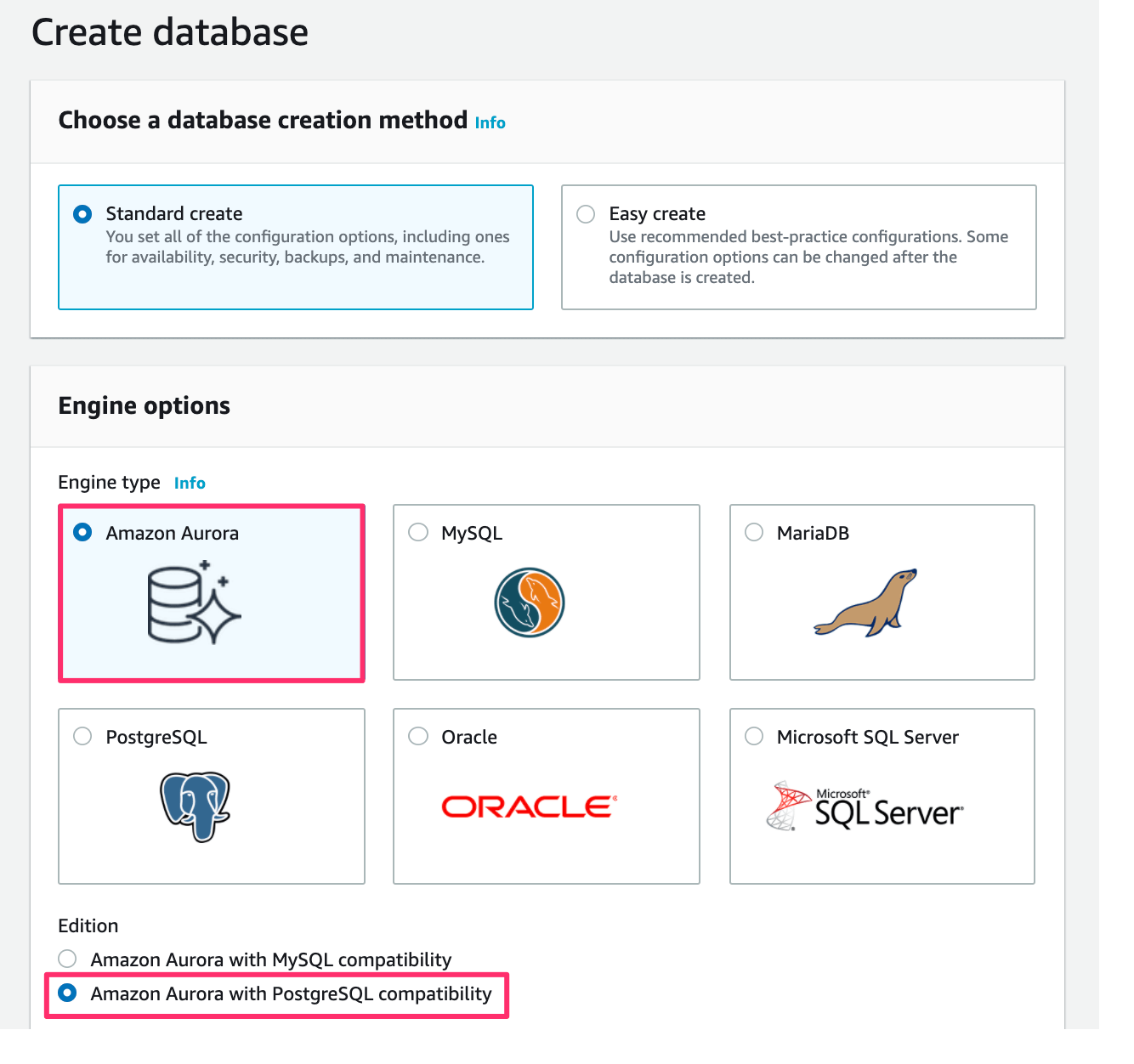
Scroll down to Settings:
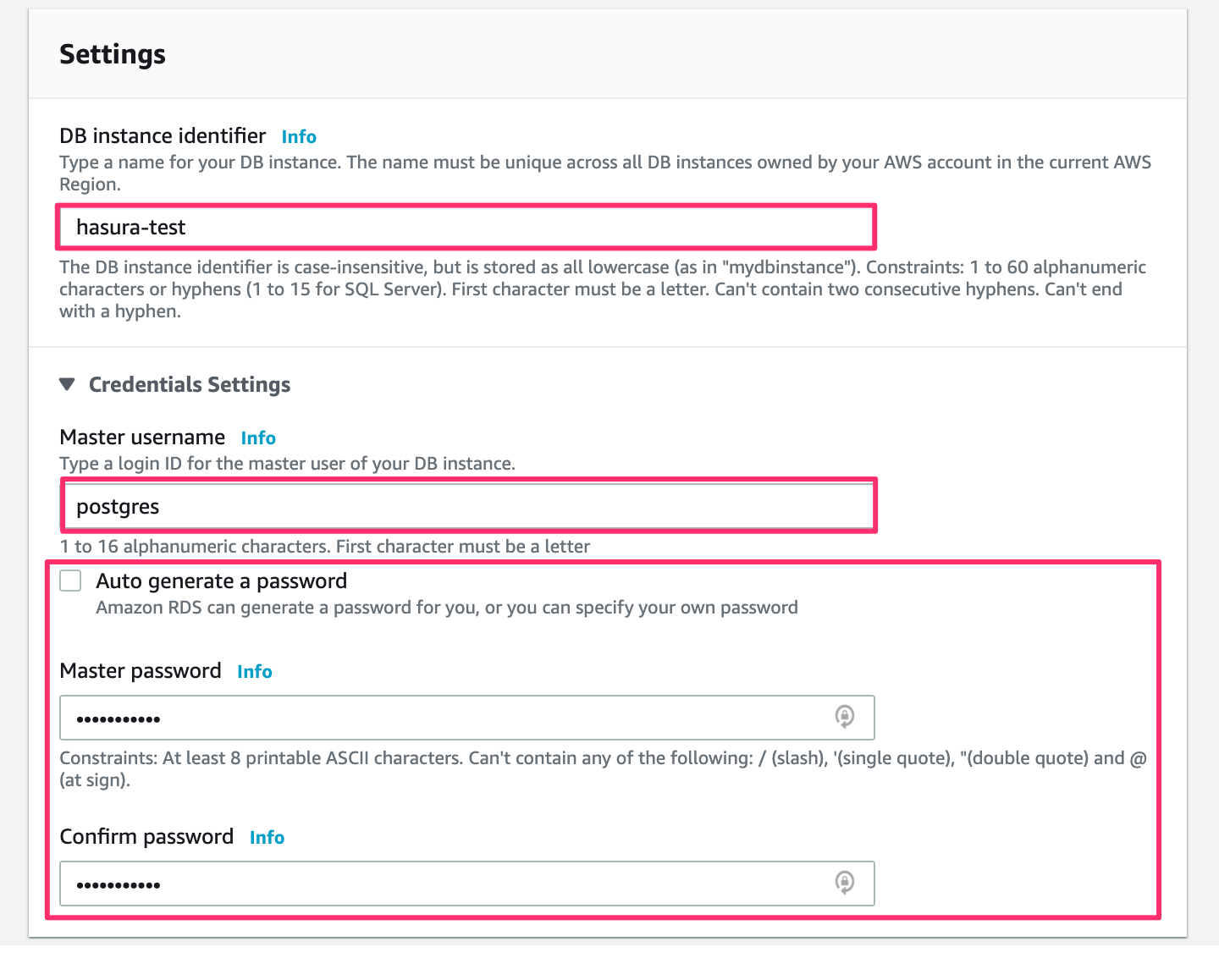
Now you can choose a DB instance identifier as a name for your database. The Master username is postgres by default.
You can change that if you have to. As for the password, you can click the checkbox for AWS to auto-generate one for you, or you can type in a password of your choice.
Scroll down and customize other database options such as DB instance size and Storage, based on your requirements.
In the Connectivity section, expand the Additional connectivity configuration. Then set Public access to Yes and choose or add a new security group:
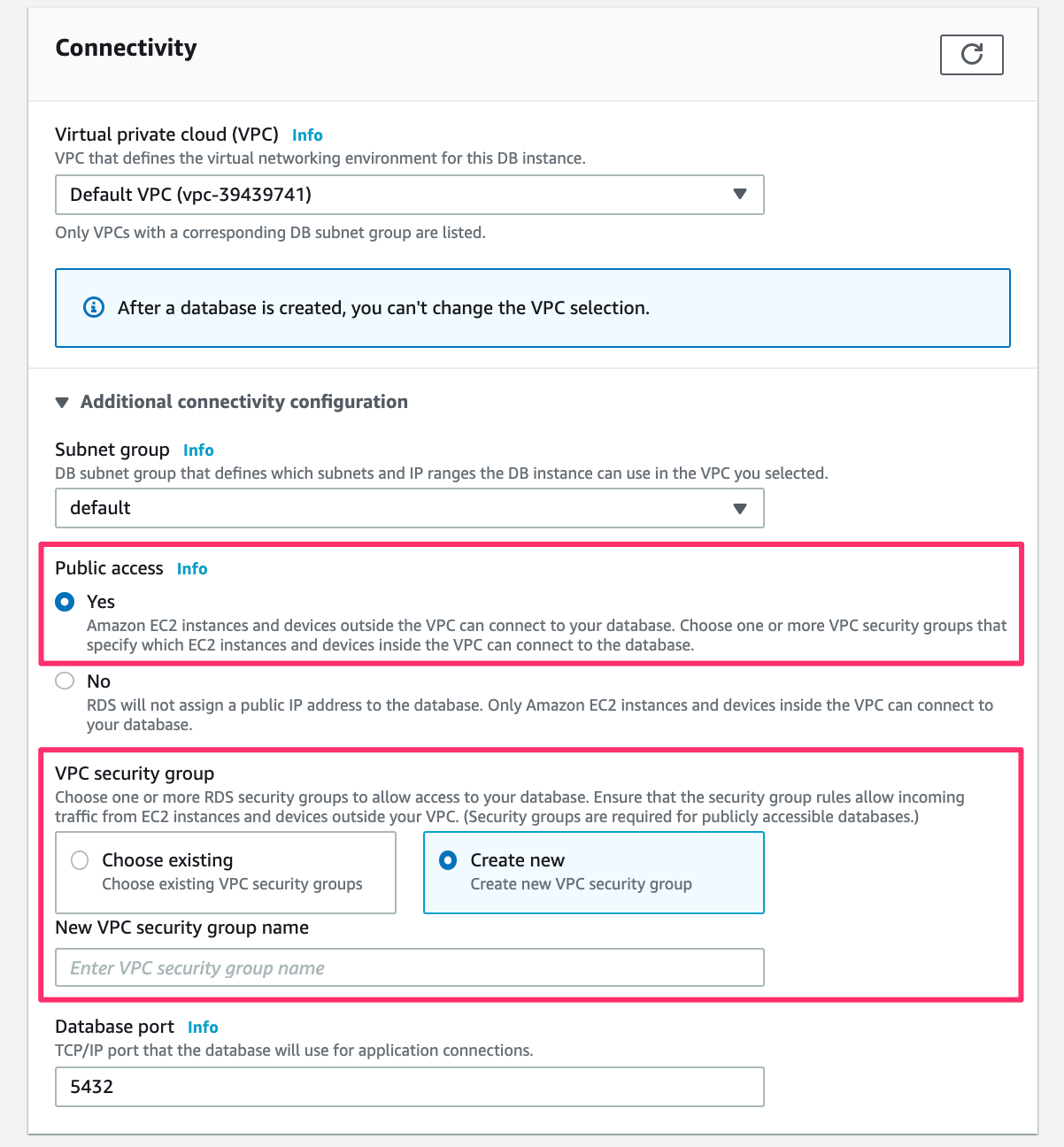
When you’re done, at the bottom, click the Create database button:
Note
If you’re using a database user other than the default one, make sure to give it the right Postgres permissions.
Step 3: Allow connections to your DB from Hasura Cloud¶
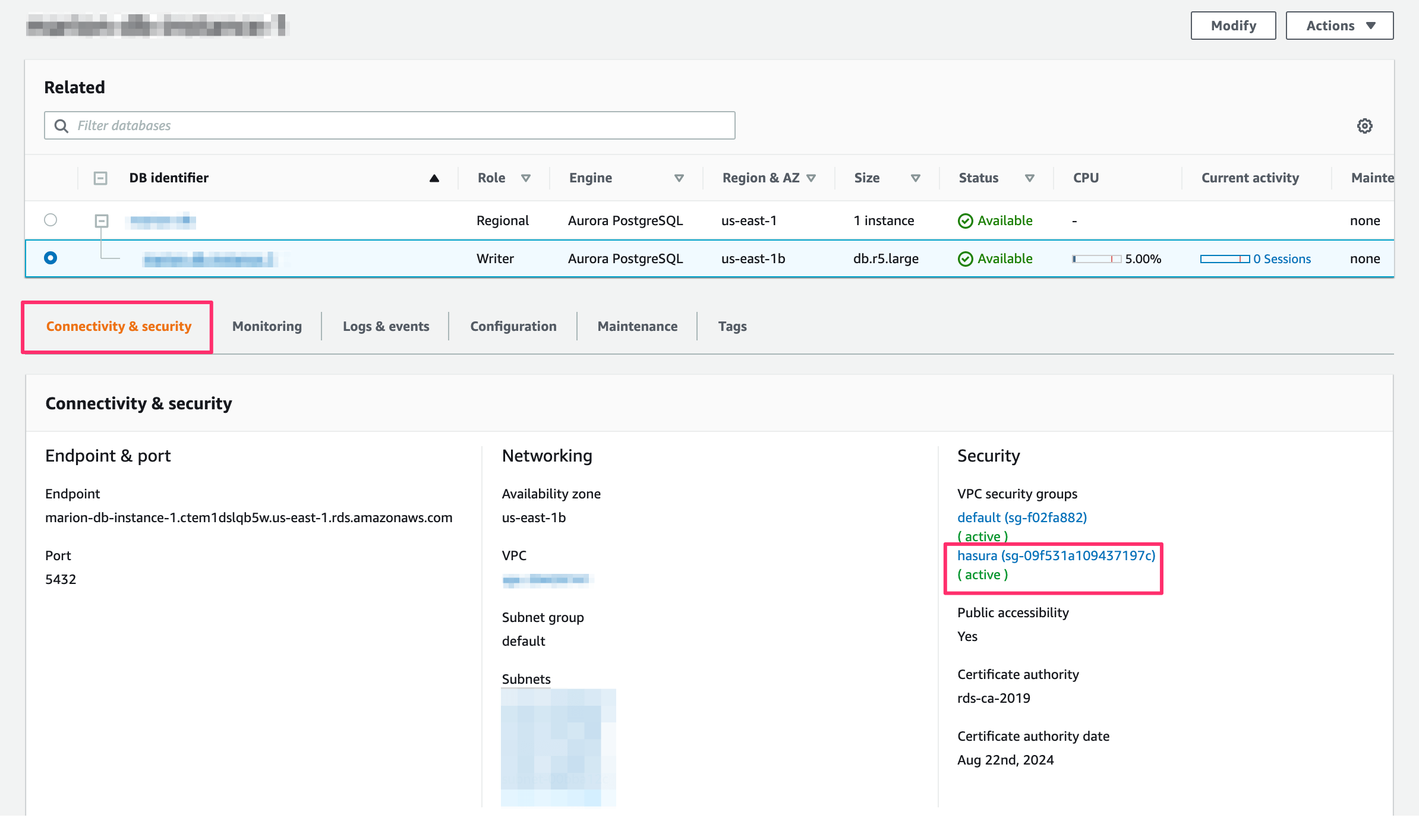
On the database dashboard, click on Connectivity & security. On the right, click on the security group that you selected or added in step 2.
Click on the security group:
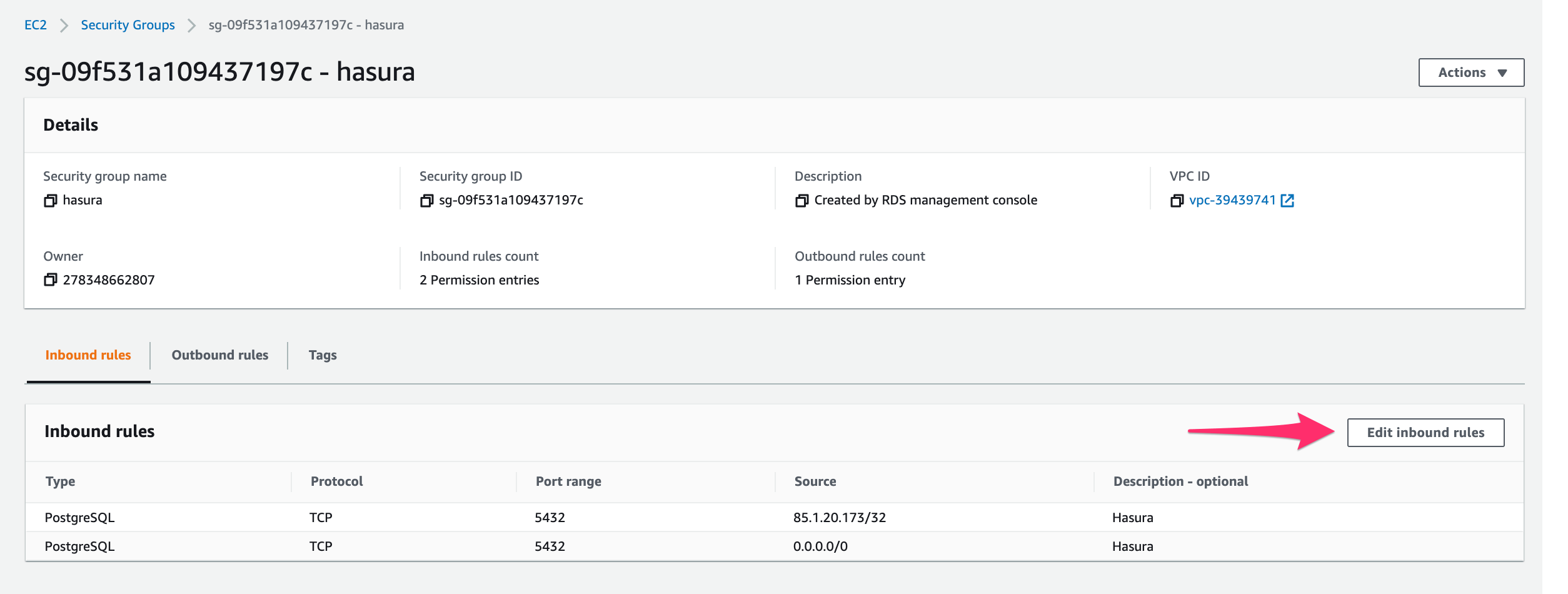
Click on Edit inbound rules:
Click on Add rule:
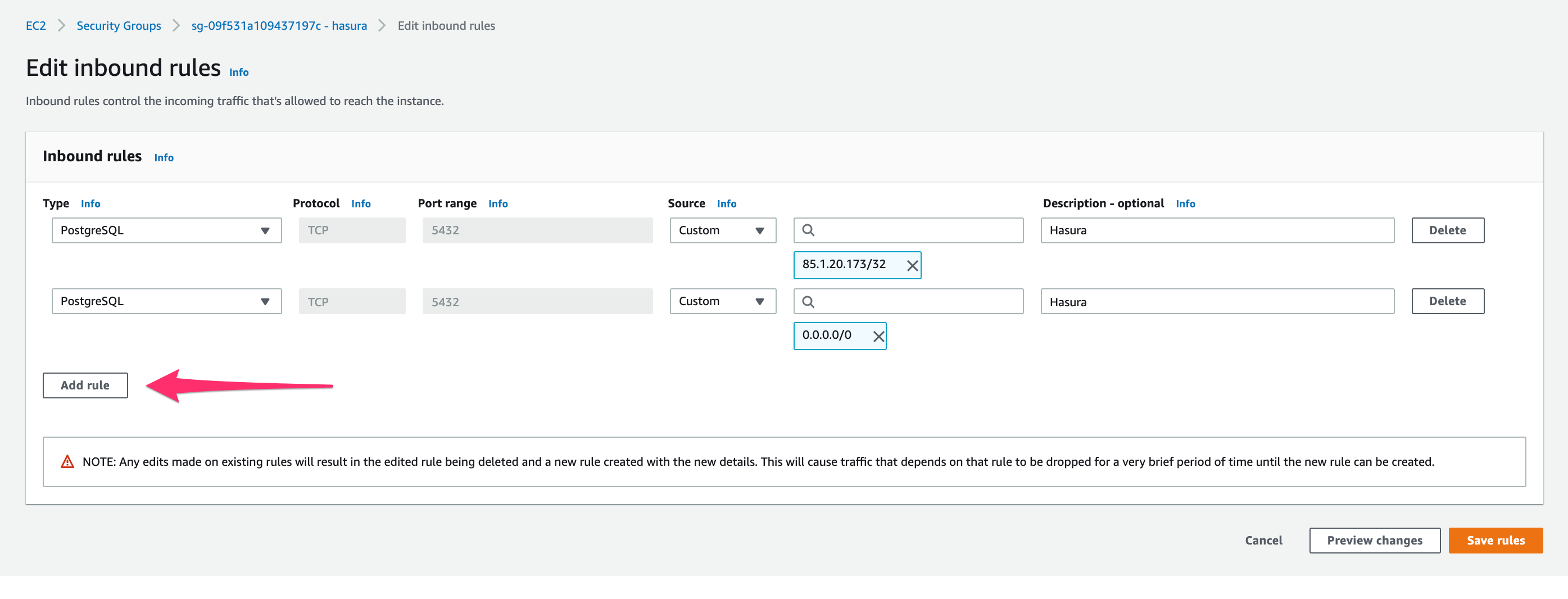
Add the Hasura IP you copied in step 1:
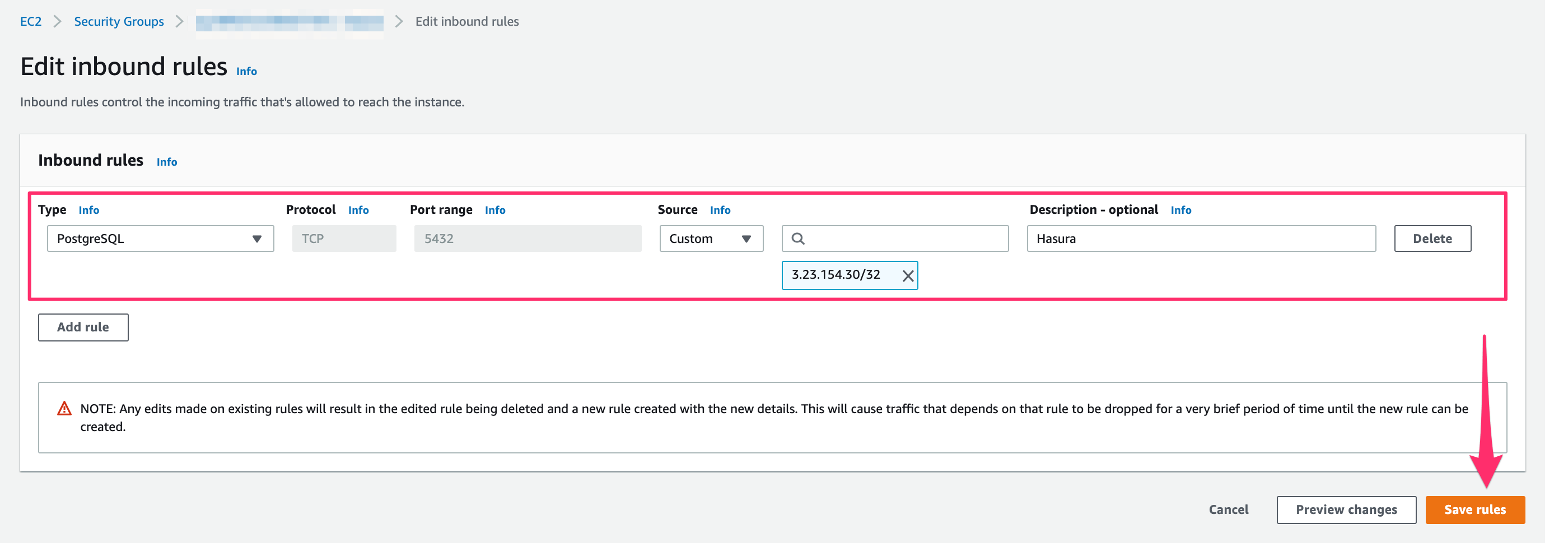
Then click Save rules.
Step 4: Construct the database connection URL¶
The structure of the database connection URL looks as follows:
postgresql://<user-name>:<password>@<public-ip>:<postgres-port>/<db>
On the database dashboard, click on Connectivity & security:
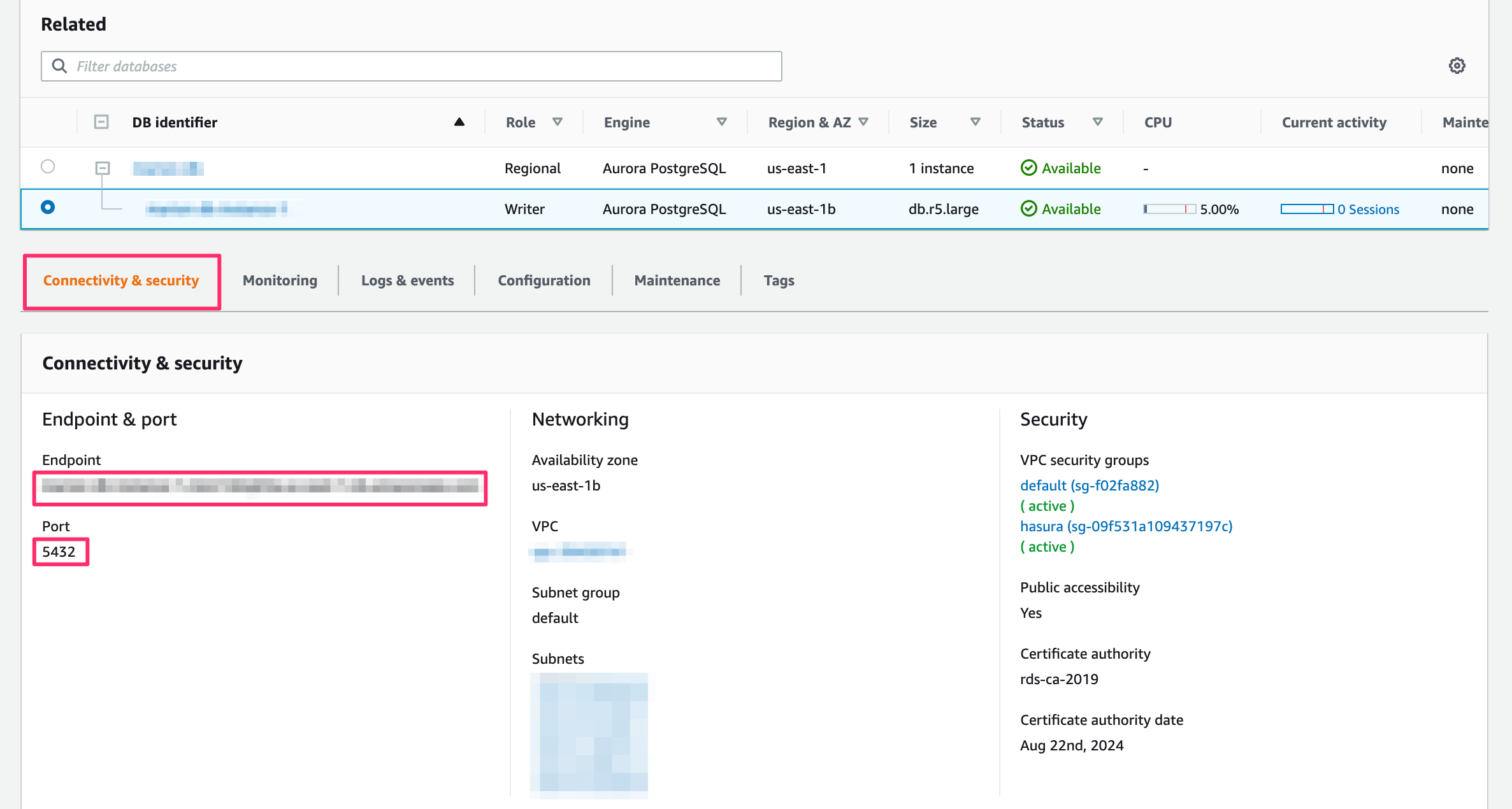
user-name: If you have a separate database user the user name will be their name. If you didn’t specify a user, the default user name ispostgres.password: If you have a separate database user, use their password. Otherwise, use the password that you chose when creating the database.public-ip: On the screenshot above, theEndpointis the public IP.postgres-port: On the screenshot above you can find it underPort. The default port for Postgres is5432.db: The DB ispostgresby default unless otherwise specified.
Step 5: Finish creating the Hasura Cloud project¶
Back on the Hasura Cloud dashboard, enter the database URL that we constructed in step 4:
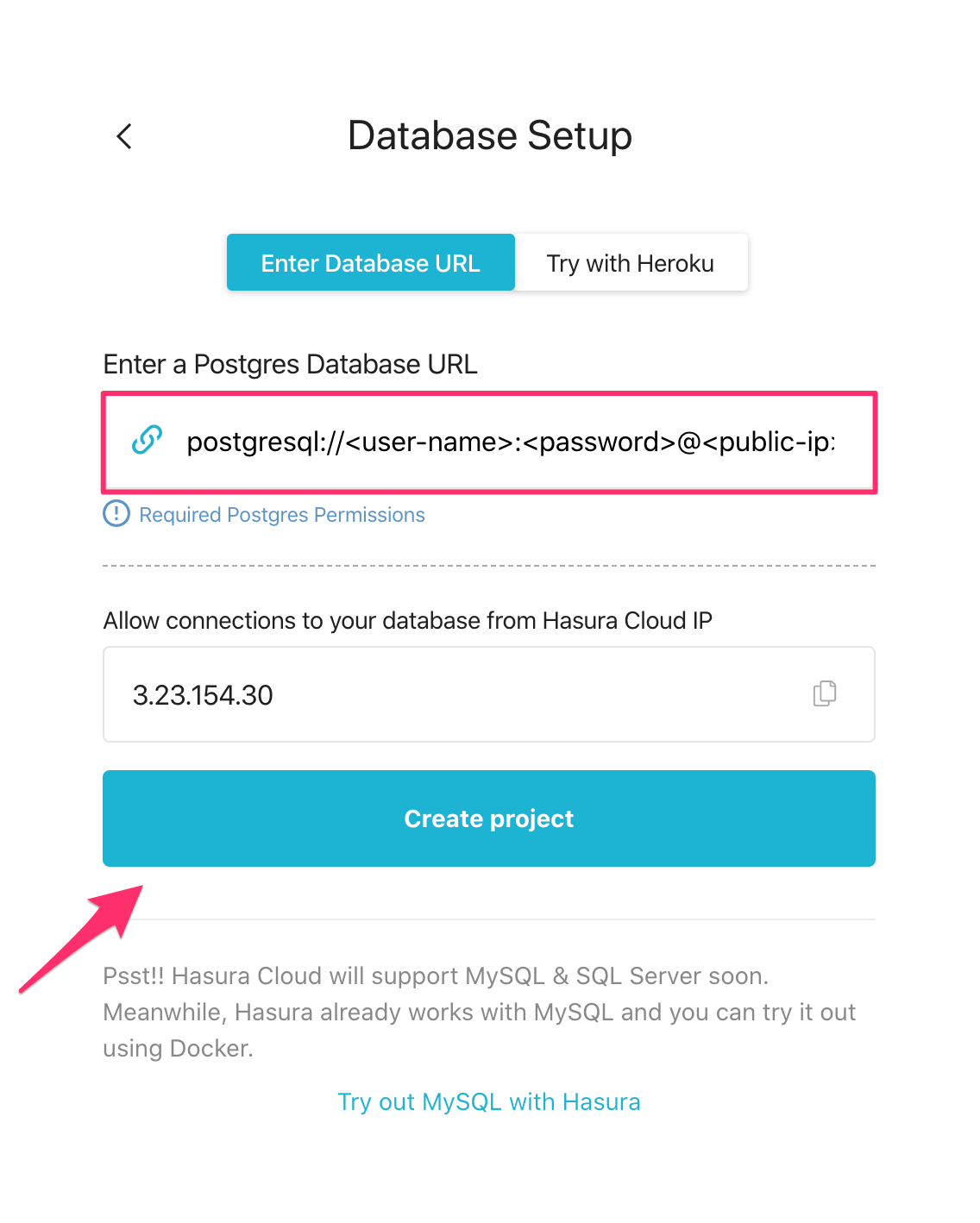
Then click Create project.
Step 6: Launch Hasura console¶
After the project is initialized successfully, click on Launch console:
Voilà. You are ready to start developing.
Next steps¶
You can check out our 30-Minute Hasura Basics Course and other GraphQL & Hasura Courses for a more detailed introduction to Hasura.
You can also click the gear icon to manage your Hasura Cloud project. (e.g. add collaborators, env vars or custom domains) and add an admin secret to make sure that your GraphQL endpoint and the Hasura console are not publicly accessible.